Product Details
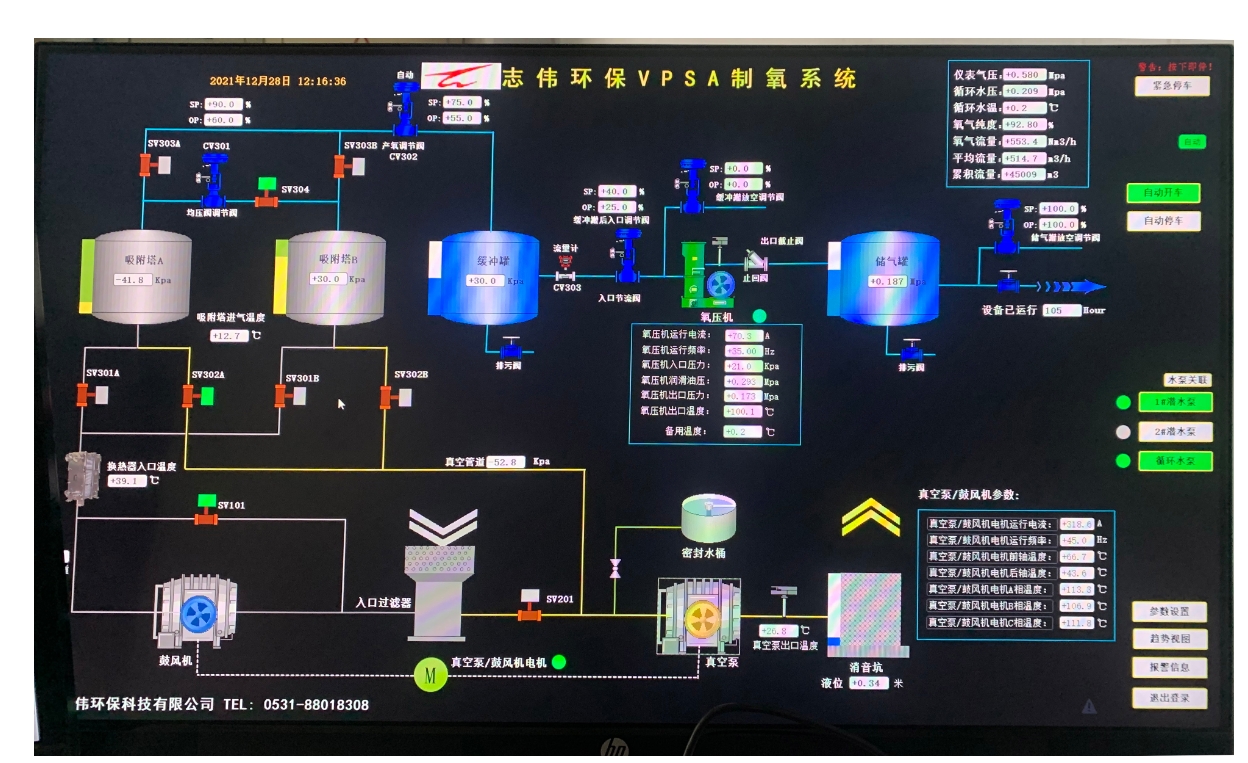
The main equipment for VPSA oxygen production includes nine parts: Roots blower, wet Roots vacuum pump, adsorber, oxygen buffer tank, switching valve, instrument control system, electrical control system, instrument air system, etc.
After removing mechanical impurities through a filter, the raw air is pressurized by a Roots blower and cooled to 30-40 ° C in an air cooler before entering from the lower part of the adsorber. In order to reduce noise, both the inlet and outlet of the Roots blower are equipped with mufflers.
There are two types of adsorbents inside the adsorber. The bottom layer of the bed is equipped with 13X molecular sieve, which is used to adsorb impurities such as moisture, carbon dioxide, and hydrocarbons in the air. Install L molecular sieve in the middle layer of the bed for the separation of oxygen and nitrogen in the air.
After entering the adsorber and passing through the 13X molecular sieve bed, impurities such as moisture and carbon dioxide in the air are adsorbed by the molecular sieve. When clean air enters the molecular bed layer, the leading air in the air is adsorbed. A large amount of oxygen that has not been adsorbed and a small amount of lead gas are adsorbed with the airflow
The outlet end of the device flows out, which is the product gas. When the oxygen purity of the product begins to decrease, it indicates that the nitrogen adsorption capacity of L molecular sieve has reached saturation. At this point, stop supplying air to the adsorber. Subsequently, the adsorber is depressurized and the airflow flows out from the lower part of the adsorber. As the bed pressure decreases, u molecules
The nitrogen adsorbed by the sieve is desorbed, and the desorbed gas is extracted by a Roots vacuum pump and discharged into the atmosphere. When the adsorber reaches a certain degree of vacuum, the molecular sieve regains its adsorption capacity.
In order to continuously obtain oxygen products, there must be at least one adsorber; At the same time, one adsorber adsorbs and produces oxygen, while the other adsorbers are pressurized or vacuum desorbed for regeneration, alternately used. The switching of operating conditions between adsorbers is achieved by pneumatic switching valves. According to the set
Time program, PLC outputs electrical signals to control the action of the solenoid valve, which is connected to the instrument air source. After the solenoid valve is activated, the instrument air enters the pneumatic switching valve cylinder, causing the pneumatic switching valve to open or close.
The product gas flowing out from the upper part of the adsorber first enters the oxygen buffer tank, and then enters the suction port of the oxygen compressor. The oxygen buffer tank serves to balance the pressure of the product.